Understanding the distinction between data and information is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Data comprises raw, unprocessed facts that need context to become useful, while information is data that has been processed, organized, and interpreted to add meaning and value. This explanation sets the stage for how businesses can transform data into strategic assets through effective knowledge management.
What Is Data?
Data represents raw elements or unprocessed facts, including numbers and symbols to text and images. When collected and observed without interpretation, these elements remain just data—simple and unorganized. When these pieces are analyzed and contextualized, they transform into something more meaningful.
Data comes in various forms:
- Quantitative data, like an item’s weight, volume, or cost, is provided numerically.
- Qualitative data is descriptive but non-numerical, such as a person’s name and sex.
What Is Information?
You get information when data is processed, organized, interpreted, and structured. The comprehensible output derived from raw data helps inform decisions, strategies, and actions. Information is essentially data made valuable and accessible—an integral component of decision-making.
For instance, if data points include daily temperature readings over a year, information is recognizing the trend of temperatures, understanding seasonal changes, and predicting future weather conditions.
What is the Difference Between Data and Information?
The transformation from data to information is fundamental in harnessing the potential of business analytics and involves several key distinctions. In its original form, data is raw and often chaotic, lacking meaningful structure or context. On the other hand, information is the refined, analyzed, and structured output derived from this data, tailored to provide actionable insights and facilitate strategic decision-making.
The journey from data to information involves several key distinctions:
- Data is raw and unstructured, like individual customer interactions or transaction logs.
- Information provides context and insights, like a trend analysis that shows increasing customer satisfaction or sales figures over time.
- Data is often abundant and readily available but can be overwhelming without interpretation.
- Information is curated and actionable, offering strategic insights to guide business decisions.
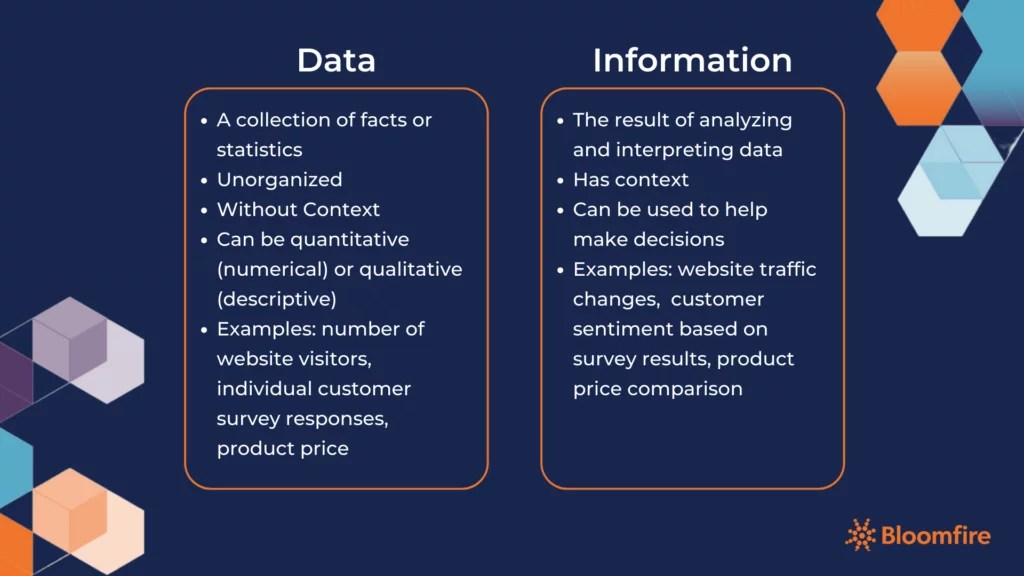
Examples of Data vs. Information
Data, represented as raw figures and observations, serves as the foundation. When processed and analyzed, this data becomes information—delivering actionable insights and strategic direction for businesses.
Data Examples
- The number of visitors to a website in one month
- Inventory levels in a warehouse on a specific date
- Individual satisfaction scores on a customer service survey
- The price of a competitors’ product
Information Examples
- Understanding that changes to a website have led to an increase or decrease in monthly site visitors
- Identifying supply chain issues based on trends in warehouse inventory levels over time
- Finding areas for improvement with customer service based on a collection of survey responses
- Determining if a competitor is charging more or less for a similar product
As highlighted, while data examples present quantitative facts devoid of context, transforming these data points into information provides businesses with valuable insights that can guide effective decision-making.
How Businesses Can Leverage Data and Information
Differentiating data from information is more than an academic exercise—it’s a strategic necessity. Businesses that excel in converting data into actionable information can enhance decision-making, optimize operations, and ultimately drive growth.
For example, analyzing customer data to understand buying patterns and preferences can lead to more effective marketing strategies, tailored product offerings, and improved customer satisfaction. This strategic use of information can significantly impact a company’s bottom line.
The Role of Knowledge Management in Maximizing Data and Information
Many organizations struggle to create a data-driven culture, often hindered by outdated or disparate information systems. This is where knowledge management platforms play a crucial role. By centralizing data and transforming it into accessible and actionable information, these platforms help organizations:
- Streamline decision-making processes
- Ensure data accuracy and reliability
- Foster a culture of informed decision-making across all levels of the organization
A robust knowledge management system stores data and organizes it into usable information, ensuring everyone can access the insights they need to make informed decisions. Understanding the qualitative benefits of knowledge management, such as improved organizational agility and enhanced employee engagement, further underscores the importance of implementing these systems beyond mere technology solutions.
Moving Toward a Data-Driven Culture
Creating a data-driven culture requires more than just access to data and information; it involves a systematic approach to knowledge management that integrates technology, people, and processes. It’s crucial to recognize the difference between technology and knowledge management. While technology provides the tools for collecting and analyzing data, knowledge management encompasses a broader strategy that includes organizing, interpreting, and using the data transformed into information.
While 26% of enterprise leaders say that all strategic decisions in their business are data-driven, another 30% say that only ‘some’ or ‘few’ are, according to an annual survey from S&P Global. Additionally, a study from Dimensional Research found that 82% of companies are making decisions based on outdated information.
Implementing a knowledge management system can help ensure that data is collected and transformed into coherent, relevant, and timely information. By adopting a knowledge management platform, organizations can:
- Enhance their operational efficiency
- Foster innovation through better access to comprehensive insights
- Improve customer engagement through data-driven strategies
Harnessing Data and Information for Strategic Advantage
Understanding the difference between data and information is crucial for any organization aiming to leverage its full potential. Businesses can effectively convert data into information to enhance decision-making processes, optimize operations, and drive strategic growth. Mastering this transformation process is critical to creating a proactive, insightful, and competitive business environment.
Embracing a systematic approach to managing and analyzing data will ensure that it transcends its raw state to become meaningful information that propels business success. This approach enhances a company’s operational capabilities and strengthens its capacity to innovate and adapt in an ever-evolving market landscape.
Embrace the Power of Knowledge Management
Discover how a knowledge management system can transform your business by effectively utilizing data and information.
Explore our KM solutions

About the Author
Sanjay Jain
One of several technology experts at Bloomfire, Sanjay and his team are responsible for the development of our platform and for advancing capabilities for digital knowledge workers to better scan, search, select, synthesize, socialize, and signify your company’s knowledge with AI.